Firefox Tweak Guide
[Page 4] Firefox Settings
This section covers the main Firefox settings which can be accessed under the Firefox Options menu screens. Before you do any advanced customization or tweaking of Firefox, you will need to understand what all of these settings do, and make sure that they are configured correctly.
Firefox Main Menu
The main settings in Firefox can be found by clicking the large Firefox Main Menu button at the top right of the browser window, also known as the Hamburger button because the three horizontal lines on it look like a hamburger. Throughout this guide it is referred to as the Firefox main menu.
There are a range of icons under this button representing the various features of Firefox. The one we will focus on right now is Options, which you should click to access the full set of key browser configuration options.
By default, the Options are now displayed as a web-like interface within a browser tab. This is just another way of displaying the Firefox options, it does not add any new settings to the Options menus. Prior to Firefox 42.0 it was possible to revert back to the older style of Options which display in a small box, by setting the browser.preferences.InContent preference to False in About:Config, however this is no longer the case.
Below we cover each section of the Options in detail, with recommendations where relevant.
General
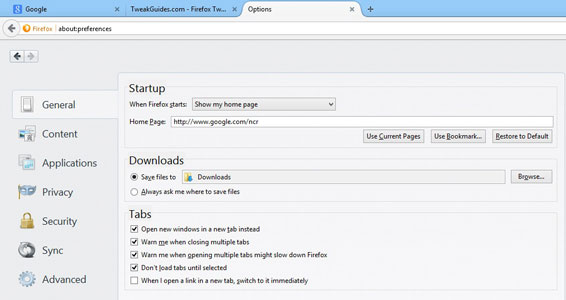
When Firefox starts: You can configure Firefox to do one of the following each time it starts: 'Show my home page' will automatically load up the website which you have entered in the Home Page box; 'Show a blank page' will simply start Firefox with a blank page; and the 'Show my windows and tabs from last time' option' will use Firefox's Session Restore feature to restore all of your open browser windows/tabs to exactly the way they were when you last closed Firefox. Select the option you prefer, but the more page(s) Firefox has to load and/or the more content-rich the page(s) are when starting up, the slower Firefox startup will be.
Home Page: If you've chosen the 'Show my home page' option under the 'When Firefox Starts' setting above, you can choose the page which appears whenever you open up Firefox. You can either manually enter a web address in the 'Home Page' box; set the page you are currently viewing as the home page by clicking the 'Use Current Page' button; or choose a page from your Bookmarks by clicking the 'Use Bookmark' button. You can set multiple homepages as well, each opening up in a separate tab when you launch Firefox or click the Home button - to do so, either click 'Use Bookmarks' and select a folder, or open the relevant pages as tabs in Firefox, then click the 'Use Current Pages' button.
Note that a default Firefox Home Page is also available which displays a Google search box, and below it a range of links to key Firefox features including Downloads, Bookmarks, History, Add-Ons, Sync, Settings and Restore Previous Session. You can access this page at any time by typing About:Home in the address bar, or by clicking the 'Restore to Default' button under the Home Page box to set it as your home page.
Save Files To: Every time you choose to download a file from the Internet with Firefox, it will be saved to a particular location on your drive. You can select to either have Firefox prompt you for a save location each time a file is downloaded by ticking the 'Always ask me where to save files' option, or you can select a default download folder by clicking the Browse button next to the 'Save files to' box, and Firefox will then automatically save all downloaded files to that location without prompting you.
Tabs
Open new windows in a tab instead: This setting essentially controls whether you use tabbed browsing or not. Whenever you click a web link on a page, if this option is unticked, the link will open as a new window in a separate instance of Firefox; if it is ticked, any new pages launched will open as a new tab within an existing instance of Firefox. I strongly recommend that this option be ticked to take advantage of tabbed browsing in Firefox, and prevent lots of instances of Firefox running. See also the browser.link.open_newwindow preference in the Advanced Tweaking section for more ways to alter this setting.
Warn me when closing multiple tabs: If ticked, this option raises a warning whenever you try to close a Firefox window containing multiple open tabs. If you're the forgetful type, or if you're used to seeing each page open in a separate window, you might want to tick this so that you don't accidentally close down Firefox when you simply intended to close a single tab. Otherwise for those familiar with tabbed browsing, I suggest unticking this option for quicker closing of Firefox windows.
Warn me when opening multiple tabs might slow down Firefox: If ticked, Firefox will warn you if you are likely to cause slowdowns or problems in Firefox by launching too many tabs at once. For the most part this depends on how much memory your system has available. I suggest ticking it to begin with, as you shouldn't be warned unless you're truly getting to the point where there are too many tabs opening up and Firefox is using too much memory to remain responsive. If you reach such a point, the best option is to close Firefox altogether and re-open it with fewer tabs open at any one time.
Don't load tabs until selected: If ticked, whenever you open multiple tabs at startup, only the content in the foremost tab will be loaded; the content in the other tabs will load once you switch to them. This setting is designed to help speed up startup time and keep Firefox responsive if you have set multiple home pages, or are restoring from a previous session. It doesn't appear to have any impact on normal tabbed browsing after startup.
When I open a link in a new tab, switch to it immediately: This option determines whether pages launched in a new tab are shown in the foreground or the background. When you open a new tab from a link on the current page (e.g. middle-clicking on a hyperlink), if this option is unticked any new tabs opened will be in the background. If ticked, your view will automatically switch to the most recently opened tab, effectively forcing all other tabs to the background.
Show tab previews in the Windows taskbar: If ticked, this option allows Firefox to display separate thumbnail previews for every open tab in the Windows Taskbar on Windows Vista/7/8 systems. If unticked, only the foremost tab will be shown in the thumbnail preview which appears when your mouse hovers over the Firefox icon in the Windows Taskbar.
Search
This section has been added to the options because as of Firefox 34.0(.5), the default search provider for any searches made via the Search bar or the Address Bar has been changed. It used to be Google for all regions, now it defaults to Yahoo for North America, Yandex for Russian locales, and Google for the rest of the world. Regardless, here you can choose which search provider to use instead of the default.
Content
Block pop-up windows: This option is designed to block "pop-up" windows, which are separate browser windows or tabs which typically open up by themselves when you open a web page, or click on certain parts of a site. They are most commonly used for advertising, and can vary in frequency, size and location. On websites for which one or more pop-up window(s) have been blocked, by default Firefox will raise a yellow warning bar stating that 'Firefox prevented this site from opening a pop-up window'. You can click the Options button at the far right of this prompt bar to determine whether you want to allow this particular site to display pop-ups, or whether you don't want this warning bar displayed again for any site with blocked pop-ups. Bear in mind that some sites have legitimate popup windows, and hence may not work correctly if you block their pop-ups. Click the 'Exceptions' button and enter the names of trusted sites you want to allow popups for in the format www.sitename.com, then click the Allow button to add each one of them.
Some popups are script-based events triggered by clicking on certain parts of a site, and are specially designed to circumvent popup blocking, so you may still see pop-ups despite the use of the pop-up blocker option. You can only block such popups if you disable Javascript as covered in the Advanced Tweaking section; or change the privacy.popups.disable_from_plugins and browser.link.open_newwindow.restriction preferences, covered in the Advanced Tweaking section; or install a script-blocking add-on like NoScript, covered in the Add-ons section. Also keep in mind that any spyware/adware resident on your PC may launch browser popups regardless of the site you visit or your browser settings, so make sure you thoroughly scan your system for malicious software. If you've disabled the Firefox pop-up warning prompt bar and want to re-enable it, see the privacy.popups.showBrowserMessage preference in the Advanced Tweaking section.
Fonts & Colors: Here you can customize the fonts, colors and styles used for various elements of web pages displayed in Firefox. For example, if you want all Sans-serif text on web pages to be Verdana, click the Advanced button then select that font in the 'Sans-serif' box. You can also change the colors used for various text and links on web pages by clicking the Colors button. The important thing to understand however is that most web pages already specify their default fonts and the styles of various elements like hyperlinks, background and text colors, etc. Therefore changing the settings here will typically have no visible impact. To ensure that your selections override the default web page options, you have to untick the relevant 'Allow pages to choose their own' boxes in the Advanced and/or Colors sections, then refresh the page to see your choice of colors and fonts implemented.
If you want to increase the font size across all web pages, then click the Advanced button, then select a size in the 'Minimum font size' box. The larger you make this value, the larger the text displayed on all web pages.
If you want to change the text rendering method in Firefox - as some people may not like the default text rendering method employed - then see the 'Use hardware acceleration when available' option under the Advanced section of the next page.
Languages: Some web pages offer different language versions which display by default when you view them. Add/Select which language you want pages to display with by default if they offer such an option. Remember that if you want a different language version of Firefox itself, for correct spell checking for example, you need to download and install the appropriate language version of Firefox to begin with - see The Basics section on the previous page of this guide. You can also download different dictionary and language packs - see the Add-ons section of the guide for details.
Applications
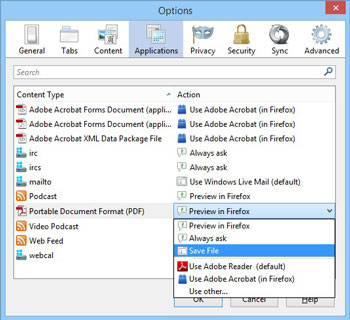
Content Type: The first time you click on certain types of file links you will be asked how you want Firefox to handle such links in the future - i.e. whether you want Firefox to always prompt you to decide; to automatically save them to your drive (if relevant); or to automatically open them, and if so, with which particular application. You may also be prompted to select whether you want your choice to become the default behavior for that particular file type when you first encounter it when browsing. Your choices are stored in this section of the Options, and you can manually come here and adjust them at any time. All the main file types and protocols that your browser has accessed so far are listed under the 'Content Type' column, and when you select the relevant content type, the behavior in the Action column becomes a drop-down menu you can use to alter as you see fit.
I recommend that where possible you change the behavior for archival file formats such as .zip or .rar, and online document formats such as .pdf and .docx to 'Save File' as the default, as otherwise Firefox will try to automatically open these file types, which can cause problems. Adobe PDF documents for example can take quite a while to load up if Firefox attempts to open them within the browser instead of downloading them. Furthermore, if a file is opened by Firefox but not manually saved by the user, it will be lost when the browser is closed.
The next page continues the Firefox setting descriptions.